Channels
Here you can manage NewAPI's upstream channels
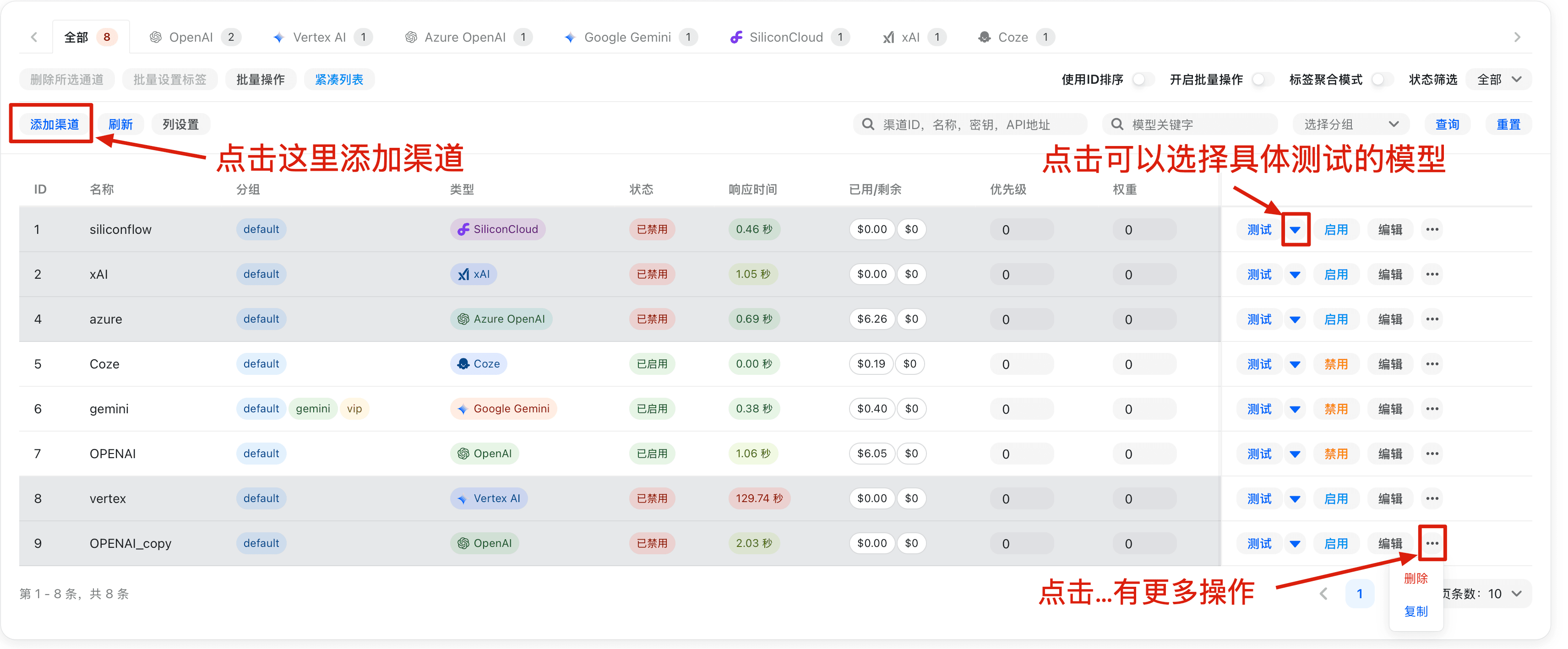
Channel Creation/Editing Page
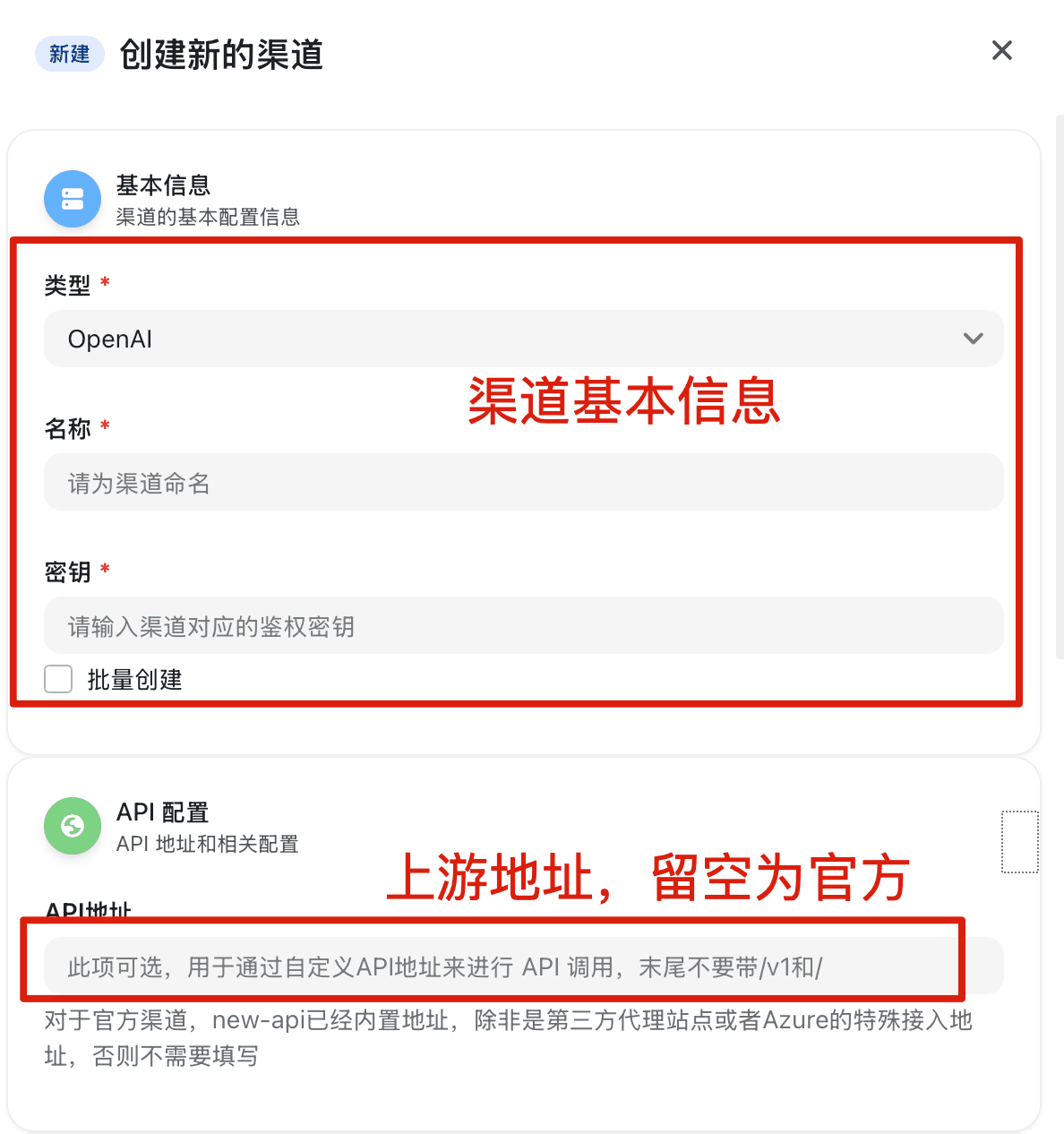
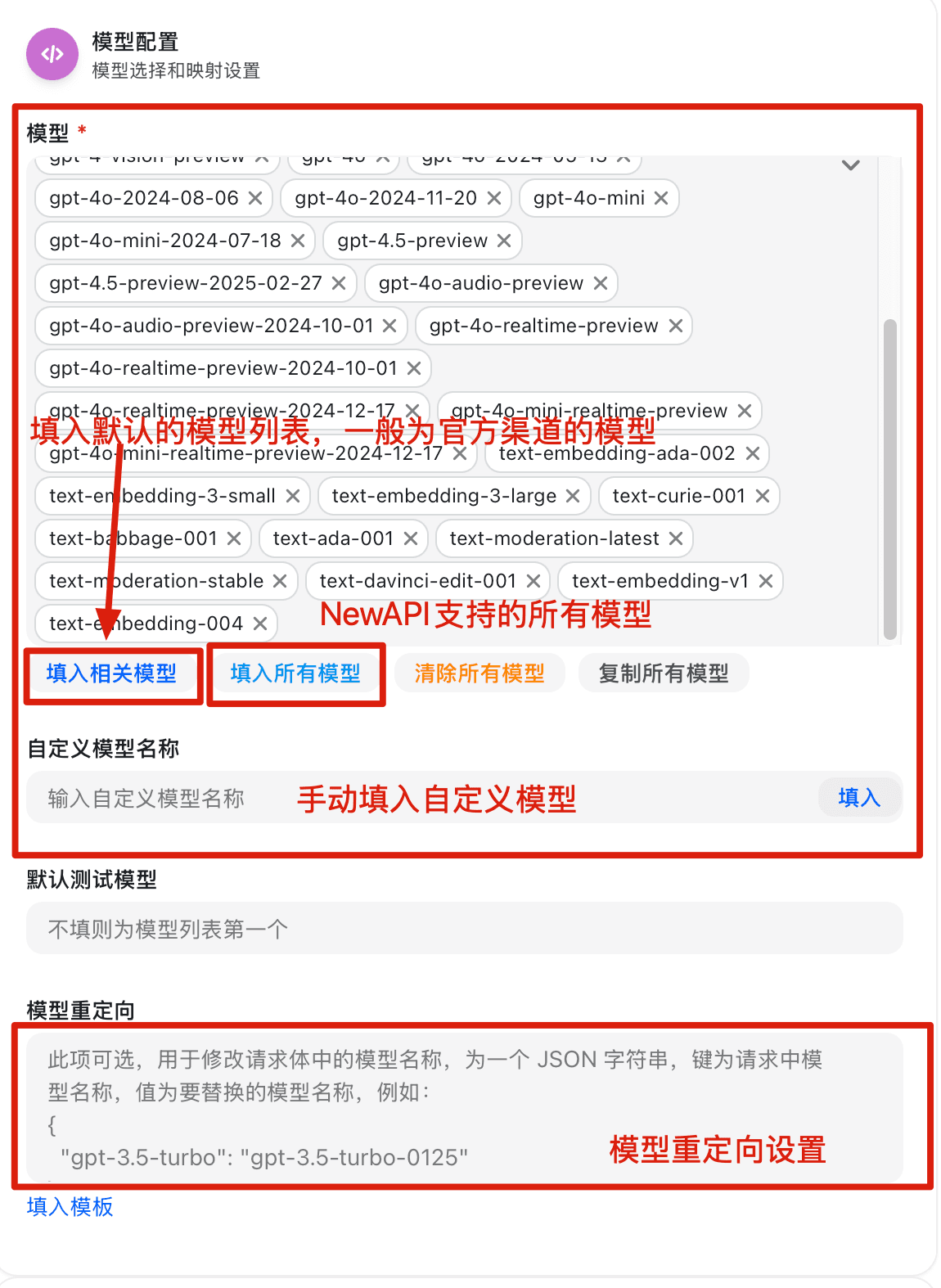
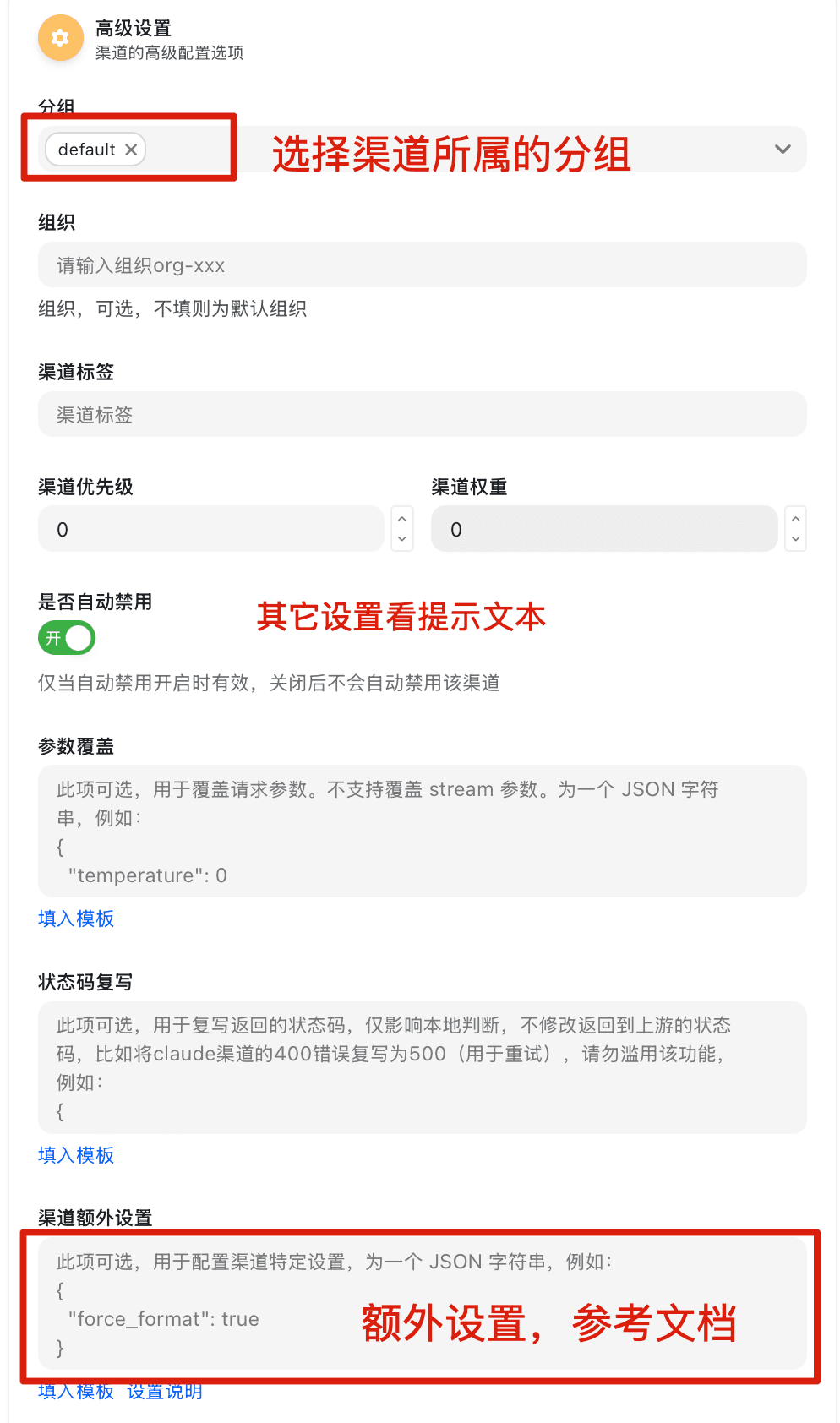
Special Channel Parameters for Coding Plan Packages
If using a Coding Plan package, the API Address field should not be filled with an actual URL, but with the corresponding special identifier:
| Package Name | Channel Type Selection | API Address (Enter Identifier) |
|---|---|---|
| GLM Coding Plan | Zhipu GLM 4V | glm-coding-plan |
| GLM Coding Plan (International Version) | Zhipu GLM 4V | glm-coding-plan-international |
| Kimi Coding Plan | Moonshot | kimi-coding-plan |
| Doubao Coding Plan | ByteDance Volcano Engine, Doubao General | Select doubao-coding-plan from dropdown |
Parameter Override Settings Documentation
Overview
The parameter override system supports two modes: simple override mode (backward compatible) and advanced operation mode. Complex dynamic parameter adjustments can be achieved through flexible conditional judgments and operation types.
Usage
Simple Override Mode
For backward compatibility, directly specify the fields and values to be overridden, and the system will merge these fields into the original request.
{
"temperature": 0.8,
"max_tokens": 2000,
"model": "gpt-4"
}Advanced Operation Mode
Define complex parameter operations using the operations array, supporting advanced features such as conditional judgments, array operations, string concatenation, and string normalization.
Basic Structure
{
"operations": [
{
"path": "temperature",
"mode": "set",
"value": 0.8,
"conditions": [...],
"logic": "AND"
}
]
}Field Description (Fill as needed):
mode: Requiredpath: Applicable toset/delete/append/prepend/trim_prefix/trim_suffix/ensure_prefix/ensure_suffix/trim_space/to_lower/to_upper/replace/regex_replacevalue: Commonly used withset/append/prepend/trim_prefix/trim_suffix/ensure_prefix/ensure_suffixfrom/to: Applicable tomove/copy/replace/regex_replacekeep_origin: Used forset(skips if value already exists) and for object merging inappend/prepend
Operation Modes (mode)
1. set - Set Value
Sets the value at the specified path.
{
"path": "temperature",
"mode": "set",
"value": 0.8,
"keep_origin": false
}Parameter Description:
keep_origin: Whentrue, skips setting if a value already exists at the target path.
2. delete - Delete Field
Deletes the field at the specified path.
{
"path": "messages.0",
"mode": "delete"
}3. move - Move Field
Moves the value of one field to another location.
{
"mode": "move",
"from": "messages.0.content",
"to": "system"
}4. append - Append Content
Appends new content after existing content.
{
"path": "messages.0.content",
"mode": "append",
"value": "\n\n请用中文回答。"
}Supported Data Types:
- String: Appends to the end of the original string.
- Array: Adds elements to the end of the array (supports adding single elements or arrays).
- Object: Merges object properties.
5. prepend - Prepend Content
Adds new content before existing content.
{
"path": "messages.0.content",
"mode": "prepend",
"value": "重要提示:请仔细阅读以下内容。\n\n"
}Supported Data Types:
- String: Prepends to the beginning of the original string.
- Array: Adds elements to the beginning of the array (supports adding single elements or arrays).
- Object: Merges object properties.
6. copy - Copy Field
Copies the value from the from path to the to path (does not delete the source field).
{
"mode": "copy",
"from": "model",
"to": "original_model"
}Parameter Requirements:
from/to: Required- An error will be reported if the source path does not exist.
7. trim_prefix - Trim Prefix
Removes the specified prefix from a string field (remains unchanged if no match).
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "trim_prefix",
"value": "openai/"
}Parameter Requirements:
value: Required
8. trim_suffix - Trim Suffix
Removes the specified suffix from a string field (remains unchanged if no match).
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "trim_suffix",
"value": "-latest"
}Parameter Requirements:
value: Required
9. ensure_prefix - Ensure Prefix
Ensures a string field starts with the specified prefix (remains unchanged if already present).
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "ensure_prefix",
"value": "openai/"
}Parameter Requirements:
value: Required and cannot be an empty string.
10. ensure_suffix - Ensure Suffix
Ensures a string field ends with the specified suffix (remains unchanged if already present).
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "ensure_suffix",
"value": "-latest"
}Parameter Requirements:
value: Required and cannot be an empty string.
11. trim_space - Trim Whitespace
Performs TrimSpace on a string field (spaces, newlines, tabs, etc., will be removed).
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "trim_space"
}12. to_lower - Convert to Lowercase
Converts a string field to lowercase.
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "to_lower"
}13. to_upper - Convert to Uppercase
Converts a string field to uppercase.
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "to_upper"
}14. replace - String Replacement
Performs substring replacement on a string field.
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "replace",
"from": "openai/",
"to": ""
}Parameter Requirements:
from: Required and cannot be an empty string.to: Optional, equivalent to an empty string if omitted.
15. regex_replace - Regex Replacement
Performs regex matching and replacement on a string field.
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "regex_replace",
"from": "^gpt-",
"to": "openai/gpt-"
}Parameter Requirements:
from: Required (regular expression, Go regexp syntax).to: Optional, equivalent to an empty string if omitted.
Conditional Judgment
Set conditions for operation execution using the conditions array; the corresponding operation will only be executed when the conditions are met.
Condition Structure
{
"conditions": [
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "contains",
"value": "gpt-4",
"invert": false,
"pass_missing_key": false
}
],
"logic": "AND"
}Condition Matching Modes
-
full: Exact match (default) -
prefix: Prefix match -
suffix: Suffix match -
contains: Contains match -
gt: Greater than (numeric types only) -
gte: Greater than or equal to (numeric types only) -
lt: Less than (numeric types only) -
lte: Less than or equal to (numeric types only) -
Note:
- Numeric comparisons can only be used for numeric types.
- String operations (prefix, suffix, contains) will convert values to strings for comparison.
Condition Parameter Description
invert: Invert function,truemeans to negate the result.pass_missing_key: Behavior when the specified path does not exist.true: Condition passes if the path does not exist.false: Condition fails if the path does not exist (default).
Logical Relationship (logic)
AND: All conditions must be met.OR: Any one condition being met is sufficient (default).
Path Syntax
Use JSON path syntax to access nested fields:
temperature- Root-level fieldmessages.0.content- Thecontentfield of the first element in the array.messages.-1.content- Thecontentfield of the last element in the array.metadata.user.name- Nested object field
Additionally, path supports the following built-in variables (which do not need to explicitly exist in the request body) and can be directly used for conditional judgments:
| Variable | Meaning | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
model / upstream_model | The target model after redirection | Conditional matching based on the actual upstream model called |
original_model | The target model before redirection | Conditional matching based on the original model requested by the user |
Practical Examples
1. Dynamically Adjust Model Parameters
Dynamically adjust the temperature parameter based on message content:
{
"operations": [
{
"path": "temperature",
"mode": "set",
"value": 0.3,
"conditions": [
{
"path": "messages.0.content",
"mode": "contains",
"value": "代码"
}
]
},
{
"path": "temperature",
"mode": "set",
"value": 0.9,
"conditions": [
{
"path": "messages.0.content",
"mode": "contains",
"value": "创意"
}
]
}
]
}2. Add System Prompt
Add a system message at the beginning of the message array:
{
"operations": [
{
"path": "messages",
"mode": "prepend",
"value": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个专业的AI助手,请始终保持礼貌和专业。"
}
]
}
]
}3. Adjust Parameters Based on Model Type
Set different max_tokens based on different models:
{
"operations": [
{
"path": "max_tokens",
"mode": "set",
"value": 4000,
"conditions": [
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "prefix",
"value": "gpt-4"
}
]
},
{
"path": "max_tokens",
"mode": "set",
"value": 2000,
"conditions": [
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "prefix",
"value": "gpt-3.5"
}
]
}
]
}4. Multiple Condition Combination (AND Logic)
Operations are executed only when multiple conditions are met simultaneously:
{
"operations": [
{
"path": "stream",
"mode": "set",
"value": false,
"conditions": [
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "contains",
"value": "claude"
},
{
"path": "messages.0.content",
"mode": "contains",
"value": "长文"
}
],
"logic": "AND"
}
]
}5. Numeric Comparison Conditions
Perform conditional judgment based on numerical values:
{
"operations": [
{
"path": "temperature",
"mode": "set",
"value": 0.1,
"conditions": [
{
"path": "max_tokens",
"mode": "gt",
"value": 1000
}
]
}
]
}6. Invert Condition
Use invert to implement inverse logic:
{
"operations": [
{
"path": "stream",
"mode": "set",
"value": true,
"conditions": [
{
"path": "model",
"mode": "contains",
"value": "gpt-3.5",
"invert": true
}
]
}
]
}7. Handle Missing Fields
Use pass_missing_key to handle potentially missing fields:
{
"operations": [
{
"path": "temperature",
"mode": "set",
"value": 0.7,
"conditions": [
{
"path": "custom_field",
"mode": "full",
"value": "special",
"pass_missing_key": true
}
]
}
]
}8. String Concatenation Example
Append instructions after the user message:
{
"operations": [
{
"path": "messages.-1.content",
"mode": "append",
"value": "\n\n请详细解释你的思考过程。"
}
]
}Notes
Execution Order: Operations are executed sequentially in the order they appear in the operations array; earlier operations may affect subsequent ones.
How is this guide?
Last updated on